Acute Wounds
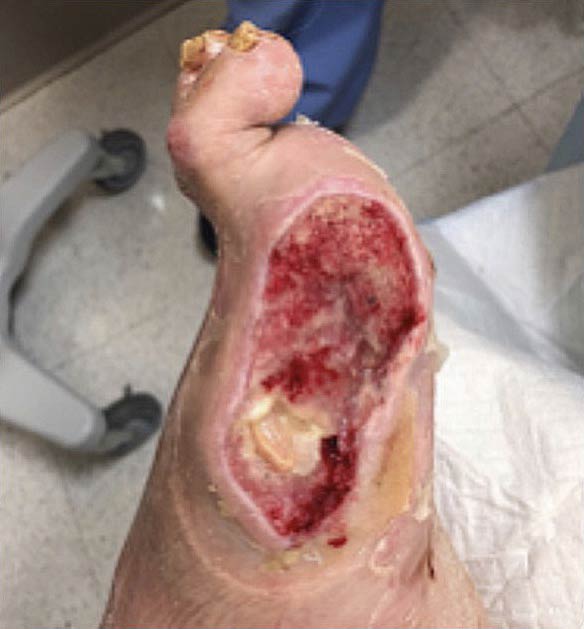
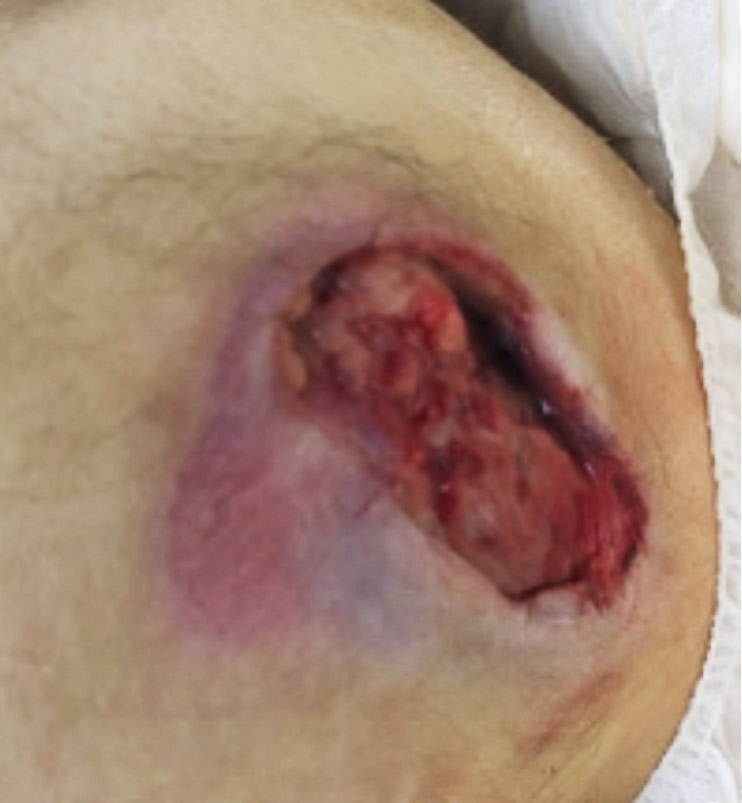
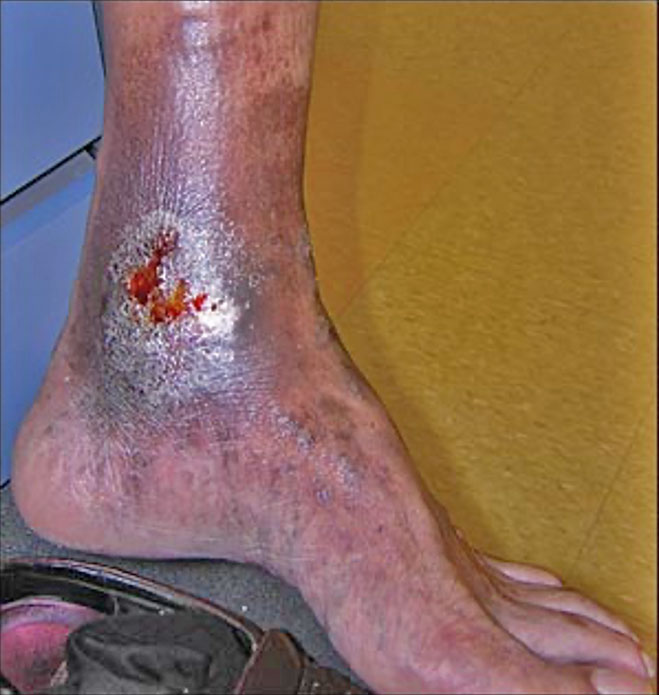
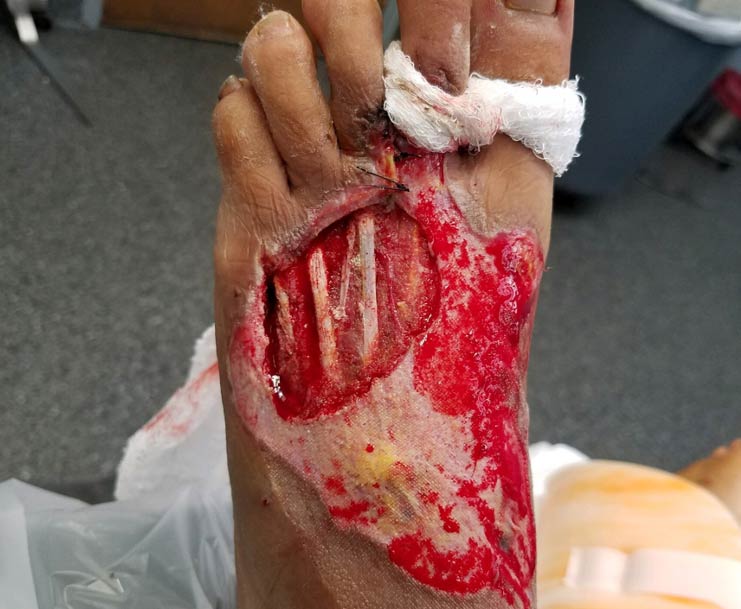
Acute wounds are recent wounds that have not yet gone through the stages of healing and include traumatic wounds, non-healing surgical wounds and burns. Similar to chronic wounds, acute wounds present a challenge to the healthcare system accounting for 17.2 million hospital, ambulatory and outpatients visits annually². Non-healing surgical wounds and traumatic wounds are the second and third most common wounds in the Medicare population¹. Non-healing surgical wounds are wounds remaining unhealed after a surgical procedure and have reported prevalence in the Medicare population as high as 3%². Traumatic wounds include acute injuries such as abrasion, puncture wounds or crush injury. There are an estimated 84 thousand surgical procedures yearly for traumatic skin wounds³. Burn injury remains a challenge despite advances in protocols and treatment options. Roughly half a million burn patients are treated annually in the US and the length of stay in the hospital for these patients is nearly double that of non-burn related stay².
¹Nussbaum SR, Carter MJ, Fife CE, DaVanzo J, Haught R, Nusgart M, Cartwright D. An Economic Evaluation of the Impact, Cost, and Medicare Policy Implications of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds. Value Health. 2018 Jan;21(1):27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Sep 19. PMID: 29304937.
²Sen CK. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021 May;10(5):281-292. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0026. PMID: 33733885; PMCID: PMC8024242.
³DiMaggio, Charles et al. “Traumatic injury in the United States: In-patient epidemiology 2000-2011.” Injury vol. 47,7 (2016): 1393-403. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2016.04.002